The Efficacy of GlideScope Video Laryngoscopy Compared with Direct Laryngoscopy in Children Who are Difficult to Intubate: An Analysis from the Pediatric Difficult Intubation Registry
BJA: British Journal of Anaesthesia 119.5 (2017): 984-992
At a Glance
Data were analyzed from the Pediatric Difficult Intubation Registry examining the use of direct laryngoscopy and GlideScope
video laryngoscopy. During difficult tracheal intubation in children, direct laryngoscopy is an overly used technique with a low
chance of success. GlideScope use was associated with a higher chance of success with no increased risk of complications.
Attempts should be minimized with either device to decrease complications.
Study Design
• Data collected, by the Pediatric Difficult Intubation Registry, from 1295 patients was analyzed
• Rates of success and complications between direct laryngoscopy and GlideScope video laryngoscopy were analyzed
Results
• Initial and eventual success rates for GlideScope were significantly higher than direct laryngoscopy
• Children weighing <10 kg had lower success rates with the GlideScope than the group as a whole
• There were no differences in complication rates per attempt between direct laryngoscopy and GlideScope
• The direct laryngoscopy group had more complications associated with the greater number of attempts needed to intubate
• There were no increased risks of hypoxia or trauma with GlideScope use
• Each additional attempt at intubation with either device resulted in a two-fold increase in complications.
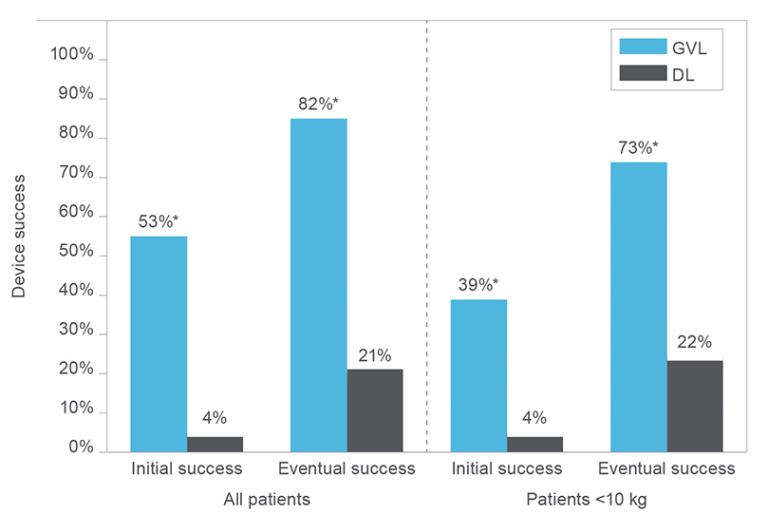
Figure 2, as Referenced in Study Initial and eventual success for GlideScope video laryngoscopy and direct laryngoscopy for all patients and patients less than 10 kilograms. *Statistically significant. For all patients and also for patients less than 10kg, GVL had significantly higher initial and eventual success rates than DL. For patients less than 10kg, GVL had significantly lower initial and eventual success rates than for all GVL patients. Rates of intubation success did not differ significantly between DL patients less than 10kg and all DL patients. GVL, GlideScope video laryngoscope; DL, direct laryngoscopy.
Park, R., et al. “The efficacy of GlideScope video laryngoscopy compared with direct laryngoscopy in children who are difficult to intubate: an analysis from the paediatric difficult intubation registry.” BJA: British Journal of Anaesthesia 119.5 (2017): 984-992.